What is pancreas: Pancreas is a gland which secrets enzymes for the digestion of food, and hormones such as insulin and glucagon to control the blood sugar level. Pancreas is located in upper abdomen behind the stomach. Pancreas is lying close to backbone or spine, that’s the reason for backache in patients with pancreatic problems.
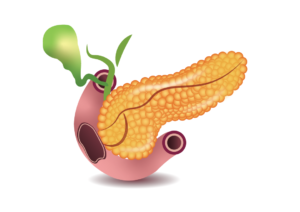
What is acute pancreatitis : Literal meaning of acute pancreatitis is sudden inflammation of the pancreas. The onset of symptoms is very fast, and within few minutes or hours, the symptoms become very severe and medical consultation is required.
What are the symptoms of acute pancreatitis
1. Sudden onset pain abdomen
2. Vomiting
3. Decrease passage of gas and flatus
4. Constipation
5. Abdomen swelling
The most common symptom of acute pancreatitis is severe pain in central abdomen above the umbilicus and below the chest pain. Pain is usually very severe and is commonly associated with pain in upper back also. Pain may get relieved by bending forward and lying prone (Lying on the stomach). The pain may be aggravated by fluid or diet, leading to reduced oral intake.



The pain of acute pancreatitis is often associated with vomiting, vomitus consists of food material and often yellow-colored bile also. Vomiting and poor oral intake may lead to decreased fluid in the body, leading to falling in blood pressure, and reduced urine, as kidneys do not receive enough blood.
Acute pancreatitis leads to a decrease in intestinal movements which leads to decreased passage of flatus and gas leading to distension of the abdomen.
Involvement of other organs in acute pancreatitis
Acute pancreatitis may affect the other organs also. Lungs, kidneys, hearts, and brain are the most common organs affected.
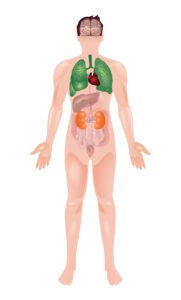
Lungs are vital organs for the maintenance of adequate oxygen in the human body. Toxins released during acute pancreatitis may affect the lungs, which may lead to difficulty in breathing and a fall in oxygen level in the blood. Not all patients with acute pancreatitis suffer from the involvement of the lung. Difficult breathing and fall in oxygen are bad signs and such patients may require ICU care.
Kidneys are vital organs for the removal of toxins through the urine. Kidneys may get affected in a few patients with acute pancreatitis, leading to decrease urine and an increase in blood parameters such as urea and creatinine.
Toxins of acute pancreatitis may affect the heart also, leading to an increase in the heart rate and fall in blood pressure.
The brain may be affected in acute pancreatitis which may lead to altered behavior and altered sensorium.
What causes acute pancreatitis. Common causes of acute pancreatitis are
1. Gall bladder stone
2. Alcohol
3. Increase lipids (triglyceride in the blood)
4. Increased calcium in the blood
5. Drug-induced
6. Virus infections such as COVID 19, mumps
7. Pancreatic tumors
8. Abdominal trauma
Common bile duct and pancreas duct open together at the ampulla in the duodenum (upper part of the small intestine). The common bile duct and pancreas duct carry bile from liver and pancreatic enzymes respectively to the small intestine, where the bile and enzymes are mixed with food for digestion. The bile duct is also connected with the gall bladder. In between the meals, bile enters the gall bladder. Sometimes the bile in the gall bladder becomes thick and leads to stone formation. Stone in gall bladder can move down in the bile duct and block the duct of pancreas leading to sudden inflammation and acute pancreatitis. Gall bladder stone are most common cause of acute pancreatitis in middle aged female. If blood level of SGOT/SGPT and serum alkaline phosphatase are increased during day one of pain, it indicates gall bladder stone as cause of acute pancreatitis. In patients suffering from acute pancreatitis due to gall bladder stone, gall bladder surgery should be done after recovering form acute pancreatitis.
Image
Alcohol consumption is a common cause of acute pancreatitis. Alcohol consumed in any form such as whiskey, beer, vodka can lead to acute pancreatitis. Acute pancreatitis can occur after sudden binge of alcohol intake.

Increased blood level of triglyceride and calcium can lead to acute pancreatitis. Calcium can be elevated due to increased Vit D and parathormone (PTH) level in blood.
Many viral infection such as mumps, COVID 19 can lead to acute pancreatitis, such patients complain of fever, body ache along with the pain.
Many drugs such as HIV medications, steroids, anti cancer medicines used to treat epilepsy can lead to acute pancreatitis.
During old age, tumors in the pancreas can lead to blockade of duct of pancreas and can lead to acute pancreatitis.

Abdominal wall trauma due to impactful contact of abdomen with hard objects such as car steering, bike handle, bicycle handle and bench can lead to acute pancreatitis.
Post ERCP Pancreatitis : ERCP is a procedure to remove the stone from the bile duct. Sometimes after ERCP, patient can develop acute pancreatitis. Post ERCP pancreatitis is mostly mild without any organ failure.
Management of acute pancreatitis
Patients with suspected acute pancreatitis should be hospitalized.
Diagnosis : Blood test in a patient suspected to have acute pancreatitis, blood test such as serum amylase/lipase level are performed. These enzymes are elevated in patients with acute pancreatitis and value can be in thousands. The level of enzymes don’t corelate with acute pancreatitis.
Imaging : USG and CT scan are performed to confirm the diagnosis of acute pancreatitis and to rule out the other causes of pain abdomen. USG abdomen and CT scan show the increased size of pancreas along with inflammation of surrounding tissue in patients with acute pancreatitis.
Treatment of acute pancreatitis
After admission to the hospital, and confirmation of diagnosis, treatment of acute pancreatitis is started.
IV fluids : Due to vomiting and poor intake, most of the patients are dehydrated, IV fluids should be started in such patients.
Medications for pain and vomiting : As most of the patients has severe pain and vomiting, medicines are started in these patients to control pain and vomiting.
Nasogastric tube placement : In patients with abdomen distension and vomiting, naso gastric tube is placed to remove gas and fluid from the stomach.
Further treatment of acute pancreatitis depend upon the severity of acute pancreatitis. Disease can be classified in mild, moderate and severe.
Mild disease is characterized by pain abdomen, without organ failure or worsening of underlying chronic illness such as Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease or Chronic heart failure.
Mild pancreatitis is treated with IV fluids and analgesics. Most of the patients usually recovers in 4-5 days can be discharged.
Moderate disease is characterized by pain abdomen, local complications such as pancreatic necrosis, fluid collection or infected pancreatic necrosis. Pancreatic fluid may leak in surrounding tissues and can form a fluid collection, known as pseudocyst and walled off necrosis.
Patients with moderate disease may require ICU or semi ICU care. These patients can develop local complications such as walled off necrosis, pseudocyst and fluid collection. Many times, these local complications improve with medical treatment only. Few patients may require drainage of local fluid collections. Three modalities endoscopy, surgery or percutaneous drain placement are available for the drainage of fluid collections. Most of the times, drainage is done after an interval of 2-3 weeks from the day of onset of pain. During this time, collections become mature and has a good wall around them. Drainage seems to be more effective after the formation of wall. Most of the patients in this group has good survival.
Severe disease is characterized by pain abdomen and associated organ failure such as kidney failure and respiratory failure.
Patients with severe disease should be admitted in ICU. Many of these patients require organ support in the form of dialysis, mechanical ventilation and medicines to increase the blood pressure. Many patients can develop infection in the pancreas and surrounding tissue, which may require drainage. Many of these patients may not improve with the treatment.